Formation AWS 09-10/03/2020
March 10, 2020
AWS Essentials
https://learning.oreilly.com/videos/amazon-web-services/9780134702186/9780134702186-awsa_01_01
1.1 Cloud Computing
On-demand Resource pooling (shared servers, shared buildings) Rapid Elasticity => growing when we need to grow Measured service => Pay as you go
1.2 Regions
Primary building block. VM, Storage, … You pick a region. Cost in AWS is determined by the region. You can choose multiple regions (for multiple audiences), or also to spread risk
1.3 Availability zones
Availability zones are a collection of datacenters. Connected with private fiber. us-west-2a us-west-2b us-west-2c … They are key to fault tolerance. System that’s resilient on the machine, but also resilient on the datacenter. What happens when a datacenter becomes unreachable.
1.4 Edge locations
Edge location Caching Amazon route 53 => DNS query as quickly as possible. Edge location serve Amazon CloudFront and they serve Amazon route 53
1.5 Scope of services
Global
AWS IAM AWS CloudFront AWS Route53
Regional
Dynamo DB …
Availability
Elastic block store Elastic compute cloud
1.6 Service overview
AWS console. top right => choose region.
Compute, Storage, Database, Networking, Analytics, Security, Management Tools, Developer tools, Internet of Things, Game development, Mobile services, … Rich environment.
2. Security in AWS
2.1 AWS Identity and Access Management
AWS IAM Authent Autho Users Group, Password Policy, Multi factor authentication => Smth you know combined with smth you have (phone (have), user/password (know)) Authenticating and Authorizing against AWS API.
Creating a user and group
Create a User
autogenerate a password AND require to create a new password at next sign in give the password to the person over an encrypted connection of some kind.
Create a group
Create a group, create permissions, and add user to the group
2.3 access keys
jane.doe password. She wants sdk, CLI, … Create Access Key for Jane.doe. Access ID, Secret Accesss key.
Permissions and Policies
Permissions are granted via policies Policies are written in JSON
We can genetare policies thanks to a tool created by Amazon.
All policies start with a default implicit deny.
We need an explicit allow to have permissions. Amazon Resource Name : Fromat pattern to find in the docs. arn:aws:iam:…:user/jdoe arn:aws:s3: arn:aws: smth can be let blank :::::
implicit deny => explicit deny => explicit allow
Statements specify : Principal (resource based policies) Actions
- ex2:RunInstanced Resources
- EC2 instances Conditions
- time of day
- from specific IP address
- resource contains particular tag
2.5 Creating and attaching policies
Generator creates the appropriate syntax. Allow EC2 RunIntances, … (actions that are authorized). ARN : * (all)
And then you can attach a policy to a group. Developers => run EC2 instances.
2.6 Understanding Roles
Rotate credentials regularly. Credentials should never be shared, in the code or in environment variables Roles enable us to use temporary credentials that are cached by the cli or the sdk. high level of security
2.7 Creating roles
IAM => Role section create new role Role Name => Name of application. myApplication Role type (S3 stuff) attach policy
every application will be able to read from S3
2.8 Federated Users
We can create Single Sign on LDAP, Active directory.
We can federate applications so that they can all use the same S3 bucket. This way we can bypass backend APIs. Allow mobile apps to access directly s3 services.
User authenticate against our app Identity broker will make a acall to aws security token service. The service will return temporary credentials.
C’est pour gérer les devs je crois (?)
2.9 managing an MFA device
Multi factor authentication Hardware MFA device (to be ordered from Amazon :o ) Virtual MFA device QR code or show secret key. Scan. Add authentication code wait add second authentication code
have jane come over to my desk.
in case you can’t call jane to you desk
2.10 Resource Policies
Apply permission to aws permissions. policies that are not applied to users or group, but to resources. Make an s3 bucket publicly readable for example.
2.11 Applying resource policy
S3 service add bucket policy click policy generator allow getObject, listObjects … arn:aws:s3:::nameofthebucket/*
add statement
2.12 Using roles for cross account access
Payer Account (initial account) (pays the bill)
Development account - Production Account
you can leverage roles. You can allow a user in one account to access ressources from another account.
2.13 Best Practices
Leverage groups : give only ENOUGH rights. Not more.
- Grant least privilege
- Strong pwd policy
- deny statements for added security
- never share credentials
- multiple accounts for isolation
master account
- protect it
- don’t use for day-to-day
- delete default access keys
- Enable MFA with physical key, and lock in a safe.
Networking AWS
Amazon virtual private cloud : VPC Segment networks Create a VPC in a particular region. Choose a particular address range We can create subnets.
3.2 Creating a VPC
from the aws console VPCs are specific to a region We have a default VPC from Amazon. 10.2.0.0 => the widest range of ip addresses
a vpc has a route table ACL => Allow incoming or outcoming traffic
3.3 adding subnets
Create a subnet below a VPC, and specify an availability zone We can assign a CIDR block (I really have to learn more about CIDR ranges !!) /24 => allows 256 IP addresses. The 1st 4, and the last one IP address are not usable (used by AWS)
3.4 Routing
ELB => load balancer
EC2 application server
Database
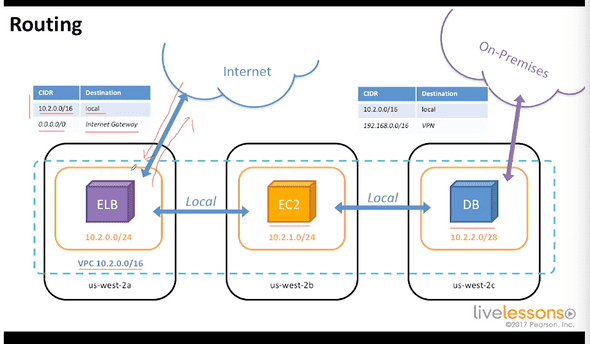 Route tables that enable to hide EC2 and database from the internet.
On premises network (what’s that ?)
Route tables that enable to hide EC2 and database from the internet.
On premises network (what’s that ?)
3.5 demo
Routing subnets to the internet. vpc dashboard => route table
Route tables associated create internet gateway attach internet gateway to vpc
auto-assign public IP => do that to enable EC2 instances
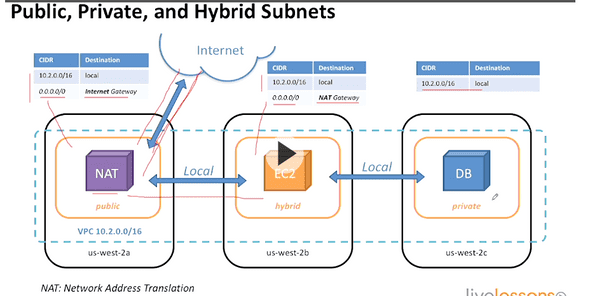
3.6 public private and hybrid subnets
3.7 Network Access Control Lists
tool to use within VPC that are stateless like a firewall arround a subnet
3.8 Security Groups
firewall that applies to an EC2 instance. it is Stateful.
3.9 creating an NACL
web traffic acl associated to vpc
inbound => rule #100 HTTP 80 TCP 80 0.0.0.0/0 ALLOW rule #101 HTTPs 443 TCP 80 0.0.0.0/0 ALLOW
outbound => rule #100 TCP 1080-65535 ALLOW (send to the internet)
3.10 Creating a security group
web-server web application security inbound rules accept http and https from anywhere NACL => subnet can receive traffic Security group => Instance can receive traffic so this is not double work
3.11 VPC peering
It is a way to pair 2 VPCs. IP ranges must not overlap Peering connection PCX routing traffic from one range to another range
3.15 Aws direct connect
dedicated private connection 1Gbps or 10 Gbps options.
4 Computing in AWS
4.1 EC2
Elastic compute cloud (EC2) Virtual machine based on Xen hypervisor Various combinations of cpu, memory, disk, IO one VM called an instance
4.2 AMazon Machine Image
bit for bit copy of root volume you launch a machine from a machine image
4.3 Launching a linux instance
Amazon images Amazon Linux 64 bits .ebs => Elastic block
t2 micro auto assign public IP tag instance to keep your environment organized Name : Linux-demo Environment : dev Application : xxx
security group !!!
download a private keypair to to access the instance public IP and private IP are associated to that instance add security group to give shell access go back to the instance, change security groups, add ssh security group port 22 in ssh should be opened
ssh -i azez.pem ex2-user@public.ip.of.instance
4.4 Key pairs
public and private keys. Way of login into the operating system. 2048 ssh2 rsa keypairs
4.5 Instance metadata service
retrieve information about an EC2 instance service within an instance to get information about itself use this instance with scripts to bootstrap stuff. The script gets information about the instance to configure software.
169,254,169,254/latest/meta-data
4.6 Demo instance Metadata Service
curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data get the instance id : export instanceId= curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/instance-id shell scripts that could access that variable.
4.7 bootstraping with userdata
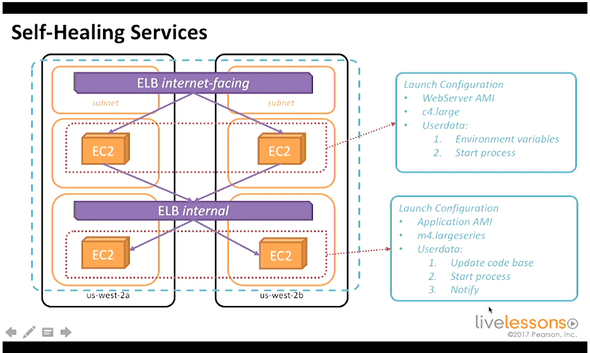
it’s the key to maintain a self healing environment
4.8 Launching a windows instance
Meh windows
4.9 Stopping and terminating instances
Stop => can restart later terminate => throw away
4.10 Billing options
on demand vs reserved instances availability is not guaranteed on reserved instances
reserved instance have a commitment (1 year, 1 or 3 year)
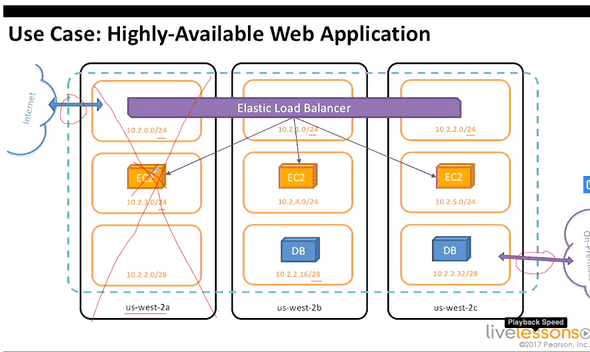
4.11 highly available web application
3 tier architecture in amazon ec2
4.12 => 4.14 Introduction to AWS Lambda
Mobile Application could access Amazon Simple Storage Service. Amazon cognito => Federated user retrieves temporary credentials
upload directly to S3.
Fire event to lambda function.
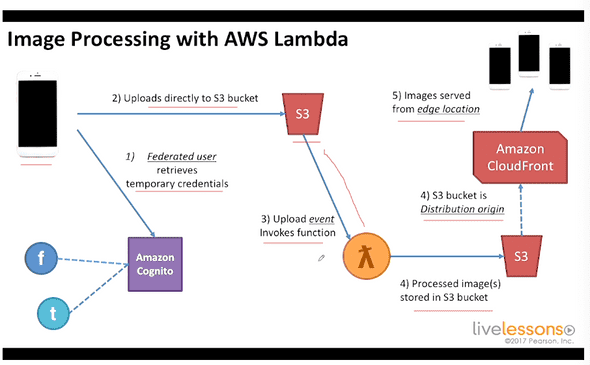
highly available and fault tolerant Speed time to market
5. Storage options
5.1 overview of aws storage options
EC2 => Instance store
block storage that are built in to the EC2 instance
storage there is EPHEMERAL.
cannot take snapshots
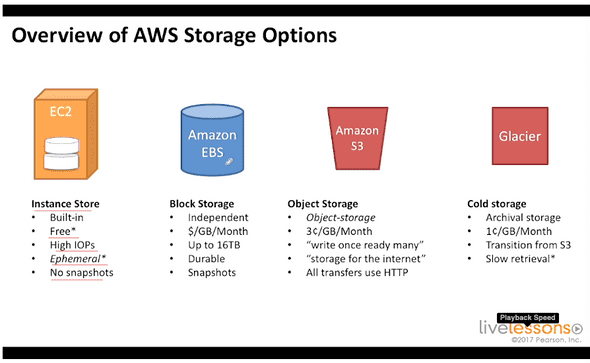
EBS => not resilient to the loss of a data center. Independant Snapshots pay per gb per month
Amazon S3 write once, read many storage for the internet for things that need to be retrieved from users
AWS Storage gateway virtual machine that is designed to be run on-premises it exposes a device
5.2 Amazon simple storage service
object storage. highly available and fault tolerant. no filesystem Bucket => Object upload limit of 5 gb objects can be multi part up to 5 TB
object storage vs block storage
5.3 Demo creating buckets and object
host static website on s3 :o :o :o
5.4 Bucket Security with resource policies
5.5 Introduction to Amazon Glacier
Write once, read rarely glacier is cold storage 3-5 hours to get the files
5.7 Demo: Adding life cycle Rules
5.8 Instance Store Volumes
they are build-in and ephemeral
5.9 Elastic block stock EBS
it is not a NAS pay for provisioned storage data is independent from instance, and is connected over network can detach and attach to another
5.11 Creating an EBS volume in the aws dashboard
volume type (HDD, SSD)
6. Databases
6.1 Options
Amazon RDS => for sql stuff, mariadb Amazon ElastiCache => Memcached, redis DynamoDB => NoSQL, Event-driven. Redshift => Encryption
6.2 Amazon RDS
Snapshots, backups and patches Read replicas for when we have read heavy traffic
6.3 Data Durability
Multi AZ deployments Primary instance with secondary standby in a different availability zone
6.4 Launch an Amazon RDS instance
subnet group => several subnets publicly accessible => NO
6.5 Amazon DynamoDB
NoSQL Data store easy noSQL service Partition vs primary key
6.7 Scan and query operations
interface pour faire des query https://learning.oreilly.com/videos/amazon-web-services/9780134702186/9780134702186-awsa_06_07
6.8 Amazon ElastiCache
Redis => in memory database, backed to disk Memcached => in memory key-value store, not backed to disk
6.9 Amazon redshift
SQL compliant. It is a clustered service parallel queries across the nodes. Ideal for OLAP and BI apps pedabyte scale data wharehouse
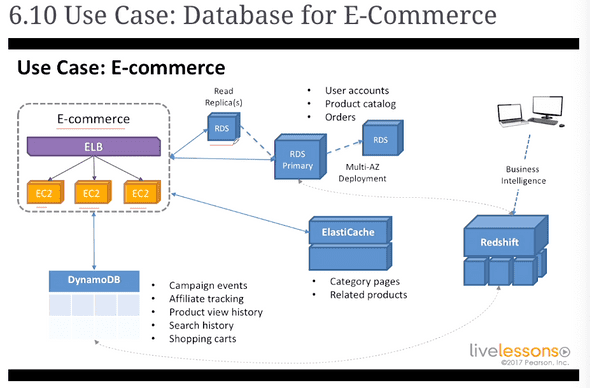
6.10 database for e-commerce
Elastic load balancer => 3 EC 2 instances
Read replica(s) Multi-AZ => Amazon handles the primary and secondary thing
ElastiCache => Category pages, related products
copies to redshift in order to run BI stuff use redshift to understand conversion rates
7 Analytics in AWS
7.1 Real time stream processing => Amazon Kinesis
“SOAP” and old school technologies from back in the 90s. Use case : warn users of the lifecycle of a pizza before it is delivered to them.
Kinesis
7.2 Real time stream processing
It divides large amount of data into usable shards. (terabytes per hour)
1 shard => 1000 PUTs per second
Kinesis stream should be handled by Apps that have ONE SINGLE PURPOSE It can be Aggregation, Sliding Window analysis,
7.3 Big data with amazon elastic MapReduce
yet another “amazing” service.
Managed Hadoop framework (or spark, presto, hbase) provision single or thousands of instance.
for data intensive applications. Data mining, log analysis, scientific simulation, genomics. can read data from anywhere.
7.4 AWS Data Pipeline
Transform data from one data type to another datatype. Helps move data between data sources. It uses EC2 or EMR to transform Data. Can Execute SQL queries, or custom applications.
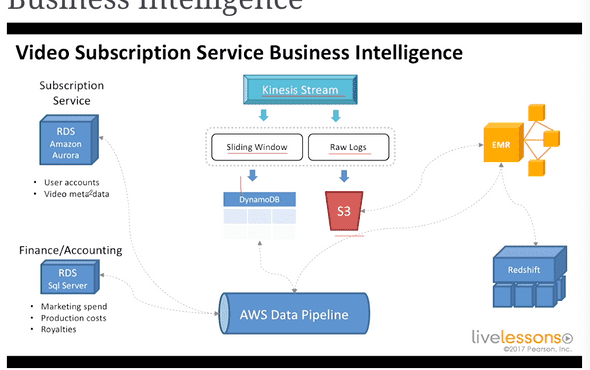
7.5 Video Subscription Service Business Intelligence
8 Developer and management tools
8.1 CloudWatch
Collect metrics on amazon stuff. It stores metrics for up to 2 weeks each service (EC2, ELB, EBS) will get its collection of metrics.
$/metric
Application-level metrics, or intance-level metrics.
CPU CloudWatch Alarms. Triggered on breach of threshold. Alarm CPUUtilization is over 80% for 2 periods of 1 minute for example
Doesn’t necessarily signal emergency.
can publish notifications. Up to 5000 alarms per account.
8.2 CloudWatch Logs
Search using specific syntax (see docs) Can search JSON fields Subscription filters
8.3 Cloudformation Infrastructure as code
Infrastructure as code cloud formation templates architectures are complex Manual process => bad documentation, difficult to reproduce Challenges with scripts => Dependencies
Solution : Automate with CloudFormation
Templates are meant to be written once and be deployed many times Parameters,
8.4 Cloudformation demo
designer within cloudformation to create templates.
Application Deployment and management
AWS Elastic BeanStalk Application management platform easy entry Ideal for developers. Super convenient Beanstalk handle resources automatically
AWS OpsWorks Configuration management platform supports chef recipes (configuration as code) based on chef recipes OpsWorks ideal for DevOps Engineers.
Launching an application on aws beanstalk
example
9. Mobile Application and services
9.1 Amazon Simple Queue service
Highly Available and fault tolerant. Seems like RabbitMQ Buffering events to enable loose coupling and asynchronous management
9.2 Amazon Simple Notification Service SNS
publish/subscribe
9.3 Amazon simple email service SES
Sending bulk email at scale Transactional emails, marketing emails, social networking get feedback about those who have been bounced, those who are marked as spam …
9.4 Amazon Cognito
Identity Integrates with major authentication providers. Enable SSO or login with social media Cognito can stor app data, state, preferences. Can store in local with SQLite.
9.5 Amazon Mobile Analytics
Makes it easy to measure usage of application. What are the going on trends? integrate AWS mobile SDK Also offers REST API.
10. High availability and fault tolerence
10.1 Elastic Load Balancing
What happens when this component fails ? Spread instances across availability zones
10.2 Listeners and SSL Certificates
Use the amazon certificate manager to have HTTPS !! Free
Upload the certificate to IAM, and then choose it for HTTPs listener
10.3 Load Balancing
Maintaining balance between availability zones
10.4 Creating an ELB
EC2 => load balancers define vps and listeners add security groups. The load balancer should have his own security group. Configure Health Check add EC2 Instances (they must be in the vpc we have chosen )
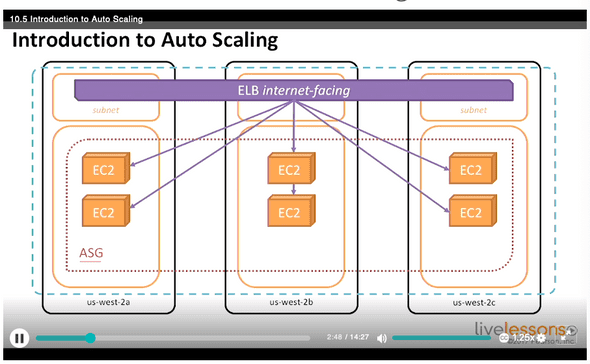
10.5 auto scaling
10.6 Demand based Scaling
Scale to meet the demand.
AutoScaling groups along with Amazon CloudWatch alarms.
Scale down when CPU is low.
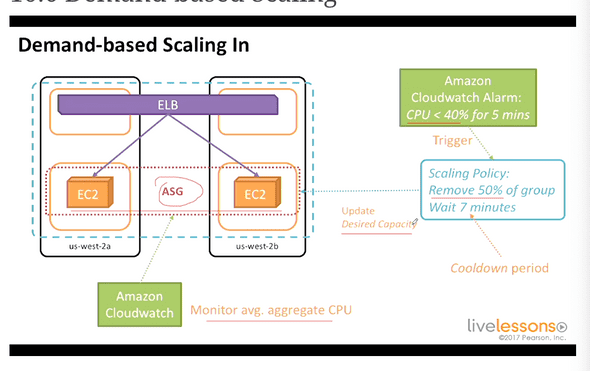
10.7 Creating an auto scaling group
- create a launch configuration yum install -y httpd to be added in create launch configuration
- Create auto scaling group select the right vpc configure scaling policies
11 Course Wrap up
11.1 The ideal
- Highly available it is up a great majority of the time AMI, EC2, S3, Auto Scaling
- fault-tolerant Aplpication continues to operate through fault AMI (?), EC2, Elastic Load Balancing
- Secure AWS CLI/Console
- Durable Data survives loss of infrastructure EBS, Snapshots, S3, Glacier
11.2 Best Practices
-
Design for Failure
- Everything will fail eventually
- any component can fail at any time
- “What happens when ”____” ?
-
Scale Horizontally
- Stateless Applications/Components (state should not be stored locally)
- ElastiCache, DynamoDB
- Distributed processsing :
- parallelize and batch
- Kinesis, Elastic Map Reduce
- Disposable resources over fixed servers
-
Automate, automate, automate !
- CloudFormation
- Elastic Beanstalk
- AutoScaling
- CloudWatch
- Third Party Tools
- Ansible, chef, puppet as ways to automate environment
-
Security in Layers
- VPS, Routes, NACLs, Security groups
- IAM: Users, groups (least rights possible), roles, keys
- Leverage multiple accounts
- Protect Master credentials
-
Loose Coupling
- Microservices
- Failures should not cascade
- ELB, Amazon SQS, Kinesis …
- Optimize for cost
11.3 The exam
80 minutes
55 questions
Architect a solution that is technically appropriate, and cost effective.